Magnesium: A Foundational Powerhouse for Human Health
Magnesium is one of the most fascinating minerals because of the fact that it is responsible for such an incredibly large number of physiological functions in our body.
the most fascinating minerals because of the fact that it is responsible for such an incredibly large number of physiological functions in our body.
From bone and heart health to playing a role in a wide variety of enzymatic reactions, magnesium can certainly be described as a foundational powerhouse for our overall health.
Here we will explore what magnesium is, its many roles within the human body, some of the best sources of magnesium, and common symptoms of deficiency to be aware of.
What Is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a macro mineral that is essential for human health. “Mg” is its abbreviation.
Minerals can be classified as either a trace element or a macro mineral.
Trace elements are needed in small amounts to fulfill their roles, and macro minerals are need in larger amounts to fulfill their roles.
Other macro mineral examples include calcium, phosphorus, sodium, and potassium.
Magnesium is also considered an electrolyte, along with the minerals sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride.
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge. Electrolytes are responsible for many vital bodily functions such as hydration, nervous system function, maintaining the acidity/alkaline balance of the body, muscle function, and more.
Most minerals work together and have significant relationships with one another.
Magnesium has a close relationship with the essential macro mineral calcium. They are antagonists, meaning when one goes up, the other goes down, but they also work together in various ways.
It is important to maintain balance between magnesium and calcium so this relationship and the many functions of each can work properly.
The Many Physiological Functions of This Foundational Mineral
Perhaps one of the most notable functions of magnesium in the body is its role as a cofactor in over 300 enzyme reactions. Cofactors are basically helpers that aid in facilitating the different biological processes that are performed by enzymes.
Enzymes (which are usually a form of protein) are catalysts in our body – they help to speed up chemical reactions in our cells.
You may have most commonly heard of digestive enzymes, but there are many more kinds of enzymes that are responsible for a very wide variety of chemical reactions in the body. These reactions can involve anything from respiration/breathing, liver function, muscle and nerve function, and much more.
Some of the enzymatic reactions that require magnesium as a cofactor include:
- Activates ATP in the mitochondria of the
 cell, which means that it helps with energy production
cell, which means that it helps with energy production - The synthesis of glutathione, one of the body’s “master antioxidants,” and a critical component of our detoxification capacity, immune function, and much more
- Blood sugar balance
- Blood pressure regulation
- Wound healing
- Making DNA and RNA
 Additional functions of magnesium include:
Additional functions of magnesium include:
- Maintaining steady heart rhythm and overall heart health
- Helps maintain bone structure and keep bones strong
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Supports digestion and bowel regularity
- Promotes mental & emotional well-being
- Supports the immune system
- Helps to balance sex hormones
Magnesium and the Stress Response
An additional important role of magnesium involves regulating a healthy stress response.
When we experience any kind of stress, be it mental, emotional, or physical, our body uses magnesium as part of its response.
This is in part because magnesium helps modulate the HPA axis which is an important part of the body’s neuroendocrine system. This stands for Hypothalamic – Pituitary – Adrenal axis. These are 3 incredibly important glands that work together to regulate many processes in the body including the stress response.
Magnesium is used within the HPA axis to help regulate the release of various stress hormones such as cortisol.
It also helps balance neurotransmitters related to the stress response.
Foods High in Magnesium
Making sure that one’s diet is full of many  magnesium-rich foods is key to ensure optimal health and wellness.
magnesium-rich foods is key to ensure optimal health and wellness.
Some of these foods include:
- Pumpkin seeds
- Almonds
- Brazil nuts (also extremely high in the mineral selenium)
- Spinach & greens such as kale, collard greens,
 turnip greens, and mustard greens
turnip greens, and mustard greens - Broccoli
- Carrots
- Black beans
- Lima beans
- Kidney beans
- Quinoa
- Yogurt
- Dark chocolate

- Avocado
- Apples
- Brown rice
- Bananas
- Chicken
- Beef
- Salmon
- Halibut
Drinking mainly spring water is also a great way to add more magnesium to your eating plan, as it contains a balanced profile of minerals including magnesium.
Symptoms of Deficiency
The symptoms of magnesium deficiency are many and can vary widely due to the large array of physiological functions that this powerhouse mineral is responsible for.
Signs and symptoms can include:
- Anxiety
- Depression
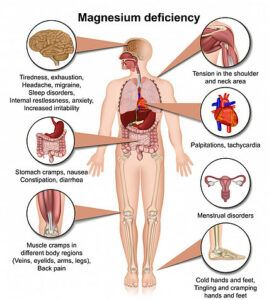
- Irritability
- Chronic fatigue
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Reduced or loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Menstrual imbalances
- Feeling weak
- Colds hands & feet
- Heart palpitations & spasms
- Chest pain
- Muscle spasms, tension, and cramps
- Seizures
- Tingling sensations
In Closing…
As we’ve explored here, magnesium is an incredibly important macro mineral that is responsible for a wide variety of significant physiological functions.
Ensuring that one’s diet includes many magnesium-rich foods is a key factor in achieving and maintaining optimal health and wellness.
REFERENCES